Another Setback for Mars Ambitions, But No Injuries Reported
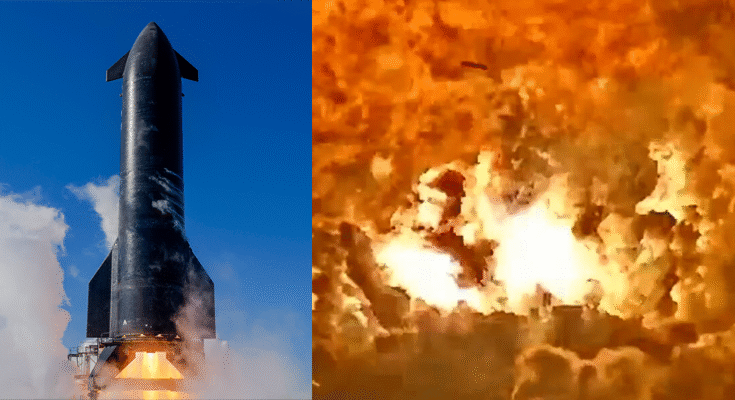
Texas: A SpaceX Starship prototype—designated Ship 36—exploded in a dramatic fireball late Wednesday night during a static fire test at Starbase, the company’s sprawling launch complex in Boca Chica, Texas. The explosion occurred just after 11 p.m. local time, moments before the rocket was expected to complete engine ignition as part of preparations for its tenth integrated test flight.
The company officially confirmed a “major anomaly” during the static fire procedures and emphasized that no personnel were injured, as all staff were evacuated ahead of the ignition. A full safety perimeter was immediately established in coordination with local authorities, and residents nearby were urged not to approach the area, though no public hazards have been identified.
Explosion Details & Initial Findings
Initial footage and satellite data suggest a double detonation, beginning near the rocket’s nosecone, followed by a larger rupture in the midsection. Eyewitnesses reported seeing a towering plume of fire and smoke that briefly lit up the Gulf Coast skyline.
Preliminary reports point toward a potential failure in a Composite Overwrapped Pressure Vessel (COPV)—a high-pressure storage unit located in the nose section of the rocket, used to house nitrogen gas. Elon Musk later took to X (formerly Twitter), describing the blast as “just a scratch”, downplaying the visible scale of the event in typical SpaceX fashion.
Safety, Response & Investigation
SpaceX has begun a joint investigation with the FAA and local emergency management agencies. Engineers are combing through telemetry data and debris to determine the precise cause of the malfunction. The site remains closed off, and the next Starship launch may face delays as infrastructure assessments continue.
A Pattern of Failures
This latest incident adds to a growing list of Starship test failures in 2025:
January: A prototype rocket exploded eight minutes after lift-off due to a faulty gimbal system.
March: A launch was aborted mid-air, leading to a temporary flight halt across multiple sites, including Florida.
May: A rocket disintegrated upon re-entry due to a fuel leak detected 30 minutes post-launch.
Despite these failures, Musk remained upbeat last month, calling the May test “a big improvement,” and reaffirming his vision to send robot-crewed missions to Mars by late 2026.
Strategic Outlook
Starship remains integral to NASA’s Artemis Moon program, and repeated failures may force further delays. Already, the first crewed Moon landing using Starship has been pushed from 2026 to early 2027. Industry observers suggest that while SpaceX’s “fail fast, iterate faster” model pushes rapid innovation, it may require tighter oversight as the missions get closer to human spaceflight.
“SpaceX Starship Explodes During Test Flight in Texas” not only highlights a single failed test, but underscores the risks and realities of cutting-edge space exploration. As the company pushes toward Mars, each setback offers lessons—though at increasing financial and reputational costs.